Scientists that created Xenobots — the world’s first living robots — have found a way to efficiently form the bots to reproduce themselves on their own.
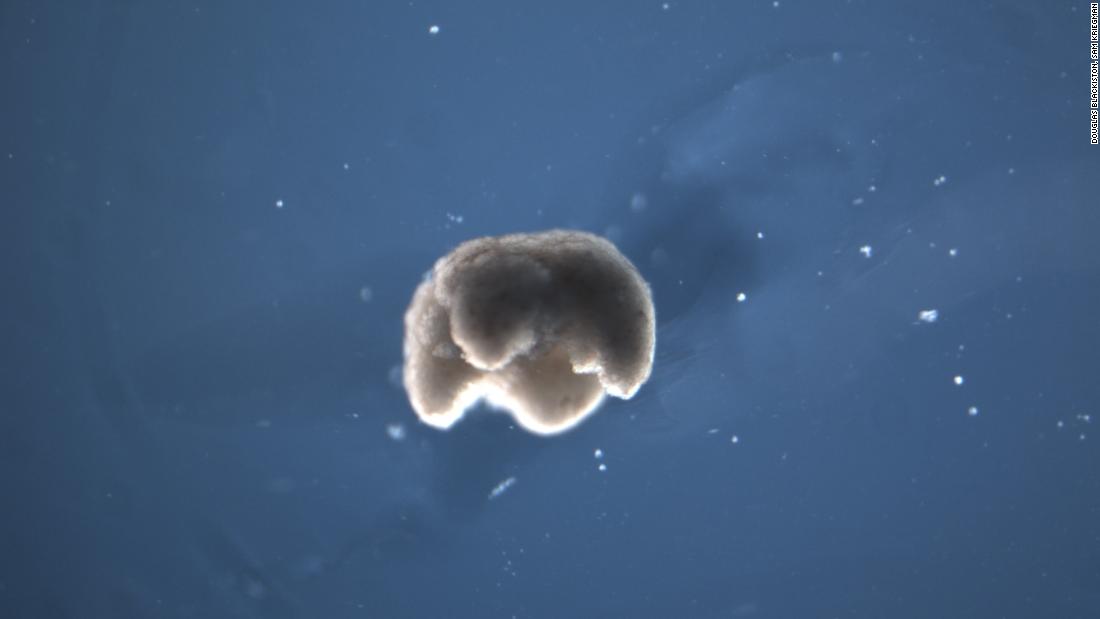
The bots are formed from stem cells of the Xenopus laevis (an African clawed frog), the cells of which have tiny little hairs called cilia to help them move around a petri dish.
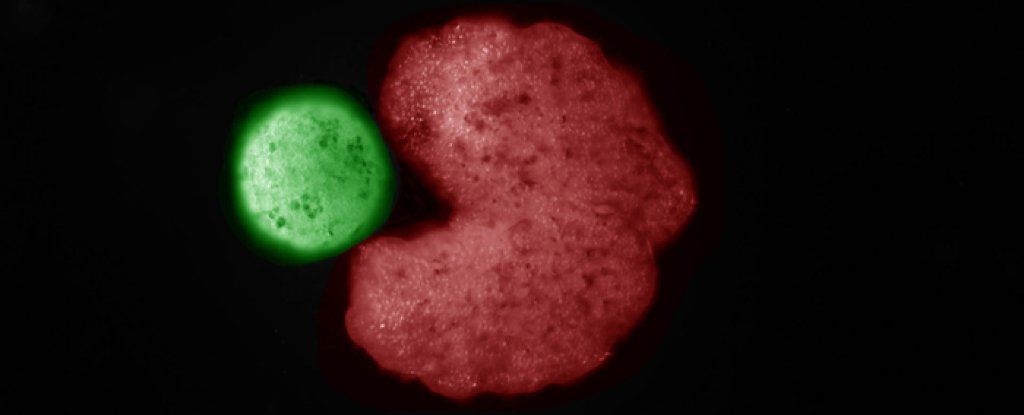
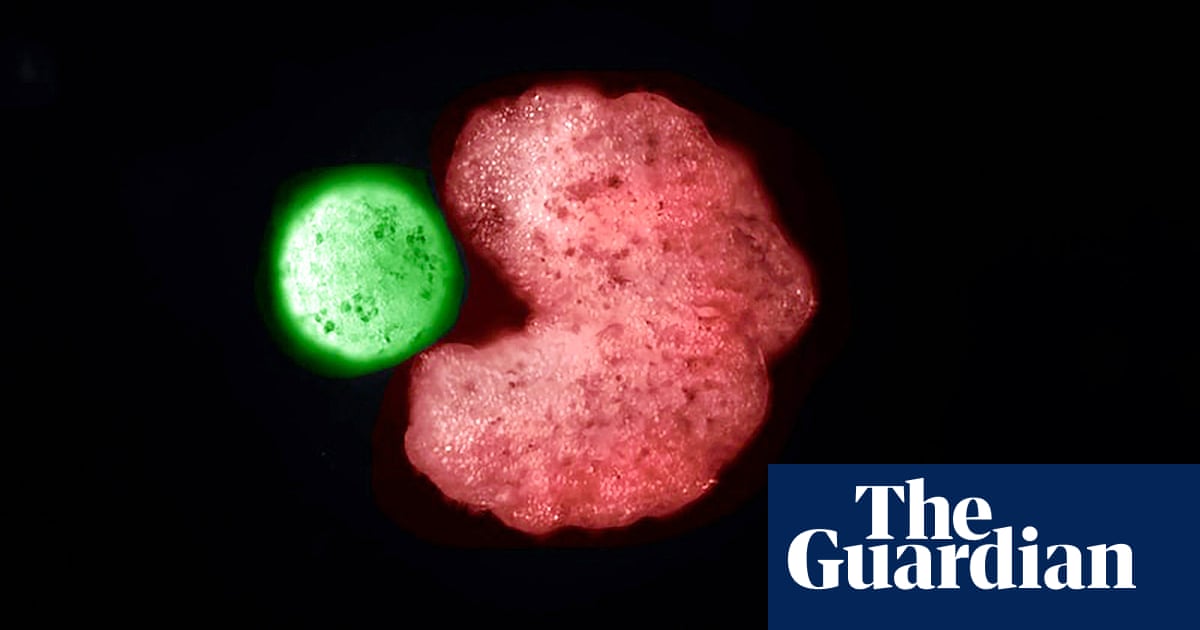
Researchers placed dye particles and silicone-coated iron beads into the dish and observed the movement of the bots, observing that they were piling up the debris.
They then repeated the process by placing additional cells – the same kind that the bots are made of — to see how the bots would react.
For now, the Xenoobots are contained to the petri dishes of the lab, but Kriegman said the next step is to develop some sensory organs to see with their eyes closed, with their own eyes closed and to swim around.
Researchers hope the project could give insight into how some animals can regenerate lost parts while some cannot, like how humans are able to regenerate parts of their liver, but salamanders can regenerate entire limbs.
‘Amazing science’: researchers find xenobots can give rise to offspring
Scientists have built the world’s first living, self-healing robots
Bizarre Creatures Are World’s First Self-Replicating ‘Living Robots’, Scientists Say