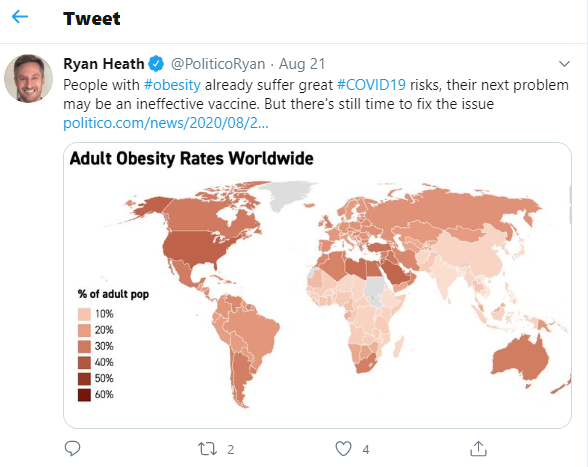
Findings from the latest study done by University of North Carolina (UNC), Saudi Health Council and World Bank indicates that obese people have an increased risk of dying from Covid-19 by nearly 50%. Diseases like diabetes and hypertension are underlying factors often associated to obesity. This, in effect, may result to a weakened immune system, making people more susceptible to the virus. Aside from this, the research also shows that the coronavirus vaccine could be less effective on people with this concerning medical problem. Some countries are already introducing new measures to control obesity.
Medicalxpress.com: A review of COVID-19 studies reveals a troubling connection between two health crises: coronavirus and obesity.

Medical Xpress.com shares a research led by University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill where concerns are raised about the impact of obesity on the effectiveness of a future COVID-19 vaccine.
A published literature on individuals infected with the virus states that those with obesity (BMI over 30) were at a greatly increased risk for hospitalization (113%), more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit (74%), and had a higher risk of death (48%) from the virus.
Obesity is already associated with numerous underlying risk factors for COVID-19, including hypertension, heart disease type 2 diabetes, and chronic kidney and liver disease.
Co-author of the literature, Melinda Beck, who is aprofessor of nutrition at Gillings School of Global Public Health further states that “Individuals with obesity are also more likely to experience physical ailments that make fighting this disease harder, such as sleep apnea, which increases pulmonary hypertension, or a body mass index that increases difficulties in a hospital setting with intubation.”