On the plains of Namibia, millions of tiny termites are building a mound of soil—an 8-foot-tall “lung” for their underground nest. During a year of construction, many termites will live and die, wind and rain will erode the structure, and yet the colony’s life-sustaining project will continue.
Inspired by the termites’ resilience and collective intelligence, a team of computer scientists and engineers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University has created an autonomous robotic construction crew. The system needs no supervisor, no eye in the sky, and no communication: just simple robots—any number of robots—that cooperate by modifying their environment.
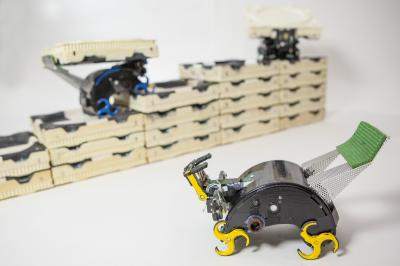
Harvard’s TERMES system demonstrates that collective systems of robots can build complex, three-dimensional structures without the need for any central command or prescribed roles. The results of the four-year project were presented this week at the AAAS 2014 Annual Meeting and published in the February 14 issue of Science.
The TERMES robots can build towers, castles, and pyramids out of foam bricks, autonomously building themselves staircases to reach the higher levels and adding bricks wherever they are needed. In the future, similar robots could lay sandbags in advance of a flood, or perform simple construction tasks on Mars.
“The key inspiration we took from termites is the idea that you can do something really complicated as a group, without a supervisor, and secondly that you can do it without everybody discussing explicitly what’s going on, but just by modifying the environment,” says principal investigator Radhika Nagpal, Fred Kavli Professor of Computer Science at Harvard SEAS. She is also a core faculty member at the Wyss Institute, where she co-leads the Bioinspired Robotics platform.