Chemical Nature of Hormones
Chemically, hormones may be categorized as either proteins or steroids. All of the hormones in the human body, besides the sex hormones and those from the adrenal cortex, are proteins or protein derivatives.
Mechanism of Hormone
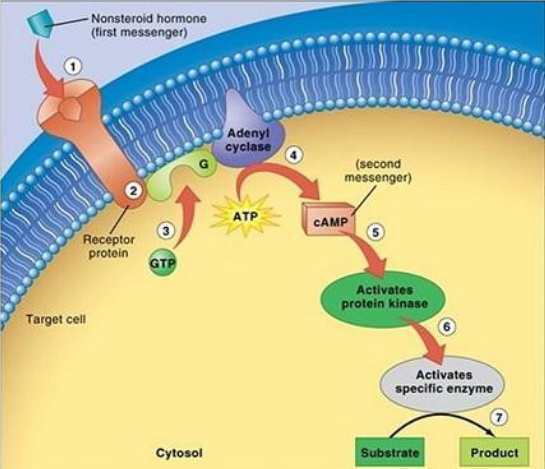
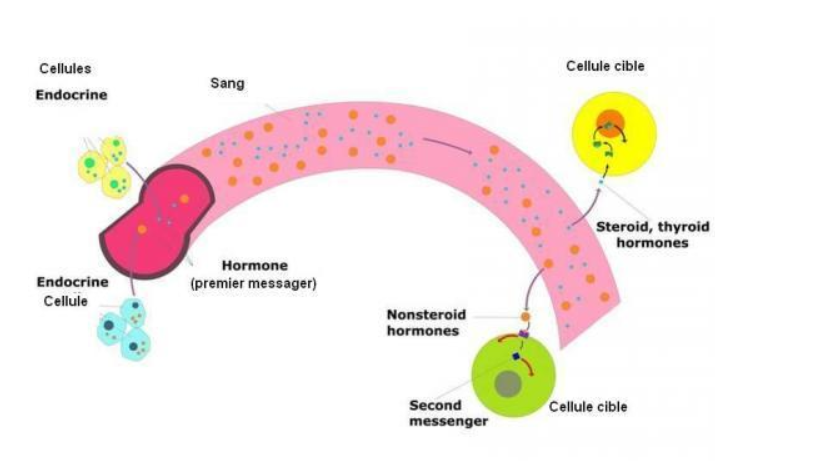
Action Hormones are taken by the blood throughout the entire body, yet they affect only certain cells. The particular cells that react to a given hormone have receptor sites for that hormone. This is a kind of a lock-and-key mechanism. If the key fits the device, then the door will open. If a hormone fits the receptor site, then there will be an impact. If a hormone and a receptor site do not resemble, then there is no effect. All the cells that have receptor sites for a given hormone build up the target tissue for that hormone. In some instances, the target tissue is confined in a single gland or organ. In other circumstances, the target tissue is dispersed and scattered throughout the body so that several areas are affected. Hormones make about their characteristic effects on target cells by altering cellular action. Protein hormones react with receptors on the surface of the cell, and the series of events that result in hormone action is comparatively rapid. Steroid hormones typically respond with receptor sections inside a cell. Because this method of action involves the synthesis of proteins, it is relatively slow.
Control of Hormone Action
Hormones are very powerful matters, which means that very small amounts of a hormone may have serious effects on metabolic methods. Because of their potency, hormone secretion must be controlled within very narrow limits to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Many hormones are managed by some form of a negative feedback mechanism. In this kind of system, a gland is susceptible to the concentration of a matter that it regulates. A negative feedback system causes a repeal of increases and decreases in body circumstances to maintain a state of balance or homeostasis. Some endocrine glands emit hormones in reply to other hormones. The hormones that cause the discharge of other hormones are called tropic hormones. A hormone from gland A causes gland B to secrete its hormone. A third means of regulating hormone flow is by direct nervous stimulation. A nerve stimulus causes gland A to secrete its hormone.
Types of hormones
Adrenaline – Stress hormone, known as the fight-or-flight hormone, stimulates the body to respond to stress by improving heart and breathing rates and preparing muscles for exertion.
Estradiol – (also known as estrogen) is the sex hormone in females. This hormone raises the growth of feminine traits (such as breasts and padded hips) and prepares the body from puberty to menopause to release eggs and nurture a developing fetus through birth. In males, this hormone helps in the development of sperm and a healthy sex drive.

Ghrelin Hunger hormone – Produced mostly in the stomach, it signals the brain that the body is running low on energy and it’s time to eat.
Insulin – Metabolic hormone that supports the body to move sugar in the bloodstream into cells where that sugar can be used as fuel.
Leptin Satiety hormone – Secreted mainly by fat cells, it signals the body when it’s had enough to eat. Leptin also signals when incoming food should be burned or deposited as fat.
Melatonin Sleep hormone – This hormone is produced by the brain’s pineal gland and readies the body for sleep.
Testosterone – Sex hormone produced by the testes in males that tells the male body to produce masculine characteristics, such as facial and body hair, a deep voice and muscle toughness. Produced in females by the ovaries and adrenal glands, it supports such traits as the growth of underarm hair.
Thyroxine – (also known as thyroid hormone or TH) Growth hormone. This is the main hormone secreted by the thyroid.
It plays a role in promoting the growth of the brain, bone, and muscle. It also helps coordinate the activities of the heart and digestive tract.
Effects on health with deficiency of hormones
· Metabolism and Appetite
· Heart Rate
· Sleep Cycles
· Reproductive Cycles and Sexual Function
· General Growth and Development
· Mood and Stress Levels
· Body Temperature
· Growth and Development
· Metabolism
· Sexual function
· Mood
Tagen Pharmaceuticals is a leading Pharmaceutical company for Hormones medications which is a fully integrated and global healthcare provider. With in-depth field expertise in the field of Hormones, it has strong skills across the spectrum of the pharmaceutical value chain. Their multidimensional commodities ranging from a wide variety of health conditions has gained a name amongst top pharmaceutical companies for providing comprehensive and entire healthcare range.