Astronomers have combined infrared and X-ray observations from two space telescopes – Herschel and XMM Newton – to create a unique look at violent events within the giant galaxy Centaurus A.
According to NASA, the observations bolster the prevailing the view that the galaxy may have been created by the cataclysmic collision of two older galaxies.

Centaurus A is the closest giant elliptical galaxy to Earth, at a distance of approximately 12 million light-years. The galaxy stands out because it contains a massive black hole at its core and emits intense blasts of radio waves.
While previous images taken in visible light hinted at the complex inner structure in Centaurus A, combining the output of two orbiting observatories working at almost opposite ends of the electromagnetic spectrum has revealed the unusual structure in much greater detail.
The galaxy was first observed by astronomer Sir John Herschel in 1847 during his survey of the southern skies. Now, more than 160 years later, the observatory bearing his family name has played a unique role in uncovering some of its secrets.
With the Herschel observatory, the giant black scar of obscuring dust crossing the center of Centaurus A all but disappears when viewed at long infrared wavelengths. The images show the flattened inner disk of a spiral galaxy, the shape of which scientists believe is due to a collision with an elliptical galaxy during a past epoch.
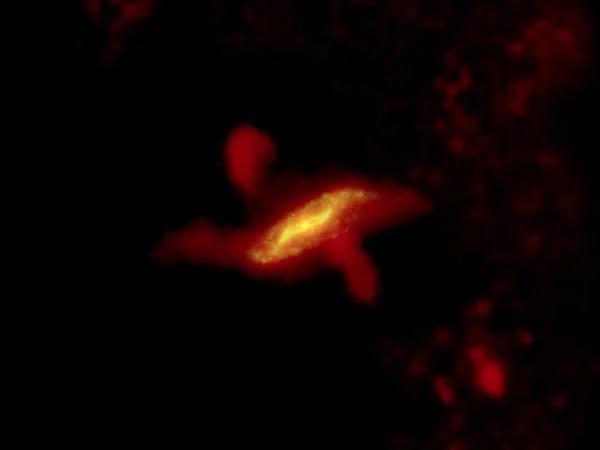
The Herschel data also reveals evidence for intense star birth toward the center of the galaxy, along with two jets emanating from the galaxy’s core – one of them 15,000 light-years long. Newly discovered clouds co-aligned with the jets can also be seen in Herschel’s view.
The XMM-Newton X-ray observatory recorded the high-energy glow from one of the jets, extending more than 12,000 light-years away from the galaxy’s bright nucleus. XMM-Newton’s view shows not only how the jet interacts with the surrounding interstellar matter, but also the galaxy’s intensely active nucleus, and its large gaseous halo.
The jets seen by both satellites are evidence of the supermassive black hole – 10 million times the mass of our sun – at the center of the galaxy.
This unique collaboration, along with observations from the ground in visible light, has provided a new perspective on the drama in objects like Centaurus A, with a black hole, star birth and the clashing of two distinct galaxies all rolled into one.